Next-Gen Packaging: Edible and Protein-Based Films

Protein-based films hold promise as the next generation of edible packaging, with the ability to encapsulate and release bioactive compounds.
Edible packaging revolutionizes sustainable food protection by eliminating the need for waste collection, processing, and recycling. Unlike traditional plastics, these materials naturally degrade and are safe for consumption, significantly reducing their environmental impact.
You can also read: The Art of Undressing: How Naked Packaging Unveils Sustainability.
While most edible packaging relies on plant-based components, recent research from China and Bangladesh highlights the promise of protein-based films. These innovative materials exhibit excellent barrier properties and effectively deliver active compounds, making them highly valuable for the food and biomedical industries.
Protein-Based Films
Protein-based films excel in coating and packaging applications due to their strong intermolecular interactions. Their excellent solubility, diverse molecular weights, and specific isoelectric points enable the creation of durable, flexible, and functional films.
Bioactive Compound Delivery
These films also stand out for their ability to carry and release bioactive compounds such as probiotics, prebiotics, and phenolic compounds. Their unique molecular structure encapsulates these compounds effectively, promoting intestinal health and boosting immune response. This multifunctional approach to food packaging supports both health and sustainability.
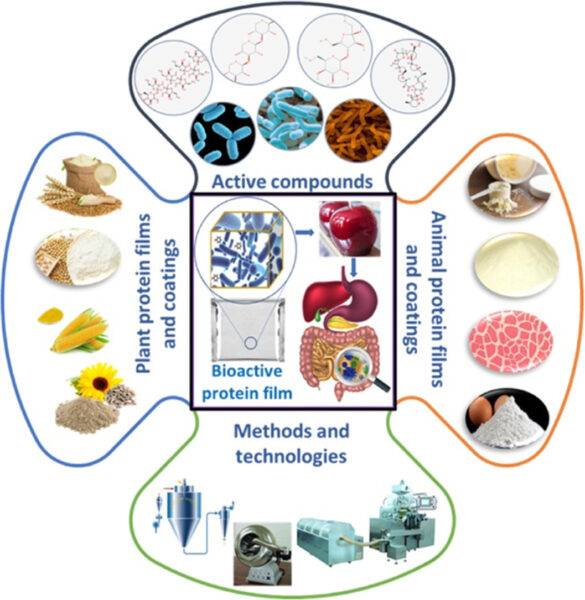
The image illustrates all the components involved in the production and processing of protein-based biofilms for delivering bioactive compounds, as well as their health benefits to the human body. Courtesy of Investigating next-generation edible packaging: Protein-based films and coatings for delivering active compounds.
Encapsulation Methods are Key
Researchers have addressed encapsulation challenges by applying multiple methods to integrate bioactive compounds into the film matrix. By carefully controlling processing, storage, and delivery conditions, they ensured compound stability and functionality. Without proper encapsulation, these compounds would degrade, reducing their health benefits. Casting and coacervation emerged as the most effective techniques, evenly distributing compounds within the films while maintaining their stability.
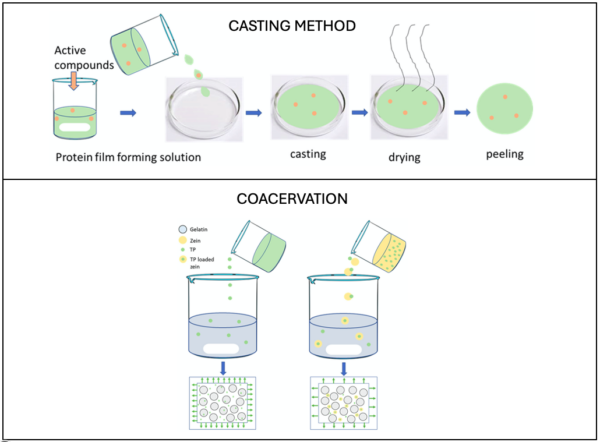
The image illustrates the two methods that yield the best results for encapsulating bioactive compounds within the film matrix. Courtesy of Investigating next-generation edible packaging: Protein-based films and coatings for delivering active compounds.
Limitations
Despite their potential, protein-based films face challenges. Their hydrophilic nature limits water resistance, making them unsuitable for certain food applications. They also exhibit mechanical weaknesses compared to synthetic plastics, raising durability concerns. Additionally, scalability and cost-effectiveness hinder their commercial adoption.
Future Directions
Innovations in protein modification and nanotechnology offer solutions to these issues. By integrating proteins with biopolymers or nanoparticles, researchers can enhance water resistance, mechanical strength, and the controlled release of active compounds. These advancements are crucial for realizing the full potential of protein-based films as a sustainable packaging solution. Researchers have made significant progress, paving the way for next-generation materials that reduce plastic waste while ensuring food safety and quality.
