Inside Materials – PVC

Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) drives innovation across industries due to its properties like exceptional cost-performance ratio, versatility, and sustainability.
PVC is the third most widely used plastic globally, surpassed only by polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP). In 2022, analysts valued the PVC market at $68.96 billion, and they project it will reach $95.88 billion by 2030. But why does PVC attract so much demand?
You can also read: Inside Materials – Polycarbonate
Key Characteristics of PVC
The secret lies in its exceptional cost-performance ratio, a critical factor in the modern industry. PVC offers cost-effectiveness and excels in high resistance, good insulation, low weight, durability, and flame retardance. Moreover, it comes in various forms, including plasticized or flexible PVC (PVC-P), unplasticized or rigid PVC (UPVC), chlorinated PVC, molecularly oriented PVC (PVC-O), and modified PVC (PVC-M), making it an incredibly versatile material. Among these, flexible and rigid PVC are the most widely recognized and used variants.
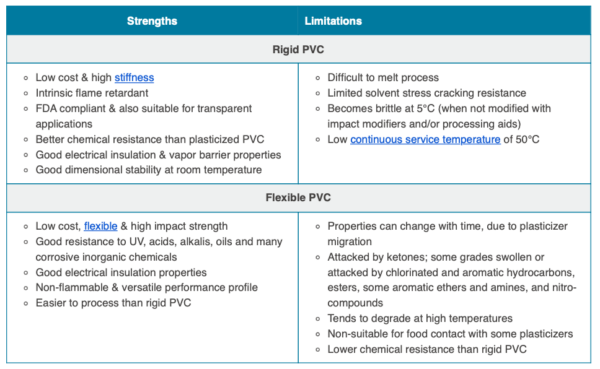
The image highlights the advantages and disadvantages of rigid and flexible PVC, the two most common forms of the material. Courtesy of Omnexus.
Versatile Processing and Product Applications
Manufacturers process PVC using techniques like extrusion, injection molding, calendaring, 3D printing, and blow molding. Each method requires specific operational conditions, which depend on the type of PVC and the additives used. This adaptability allows PVC to suit a wide range of applications. These include pipes for drinking and wastewater, insulated cables and wires, medical devices, and products like clothing and footwear.

PVC’s Role in Sustainability
Regarding sustainability, PVC impacts the environment less than many other plastics. This is due to its long lifespan, which ranges from 10 to 50 years. PVC is 100% mechanical and chemical recyclable and carries the recycling code #3. Various initiatives aim to enhance and promote PVC recycling, such as:
- +Vantage Vinyl from the Vinyl (PVC) Institute in the U.S., which advocates for recycling practices and sustainability.
- Recovinyl from the European PVC Value Chain, which focuses on improving PVC waste collection and recycling in Europe.
- PVC Stewardship Program from the Vinyl Council of Australia, which establishes standards for managing PVC’s environmental impact.
- Eco Responsible from the Vinyl Institute of Canada drives efforts for recycling and environmental responsibility in Canada. It achieves this through a management certification program.
Industry Leaders Driving PVC Innovation
PVC is a highly versatile and valuable material across industries like construction, packaging, plumbing, and electrical insulation. Its adaptability to various applications, along with a strong focus on sustainability, positions PVC as an attractive option for many industries. Leading companies in the PVC industry, such as Formosa, Ineos, Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., and Westlake Corporation, have recognized this potential. They have effectively harnessed it to advance their operations and drive industry innovation.
