Combining Lean Thinking and LCA for Sustainable Manufacturing

Researchers have developed a novel approach combining Lean Thinking and Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), significantly reducing plastic products’ negative environmental impacts.
To address these issues, researchers have created a new method that integrates Lean Thinking with Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), effectively reducing the environmental impacts of plastic products.
Integrating Lean and LCA in Plastic Injection Moulding
Lean manufacturing techniques, originating from the Toyota Production System, have transformed industrial production by eliminating waste and focusing on continuous improvement. These methods emphasize efficiency and cost reduction without compromising quality, which is crucial for the competitive plastics industry.
Fundamental techniques include Value Stream Mapping (VSM) to identify and eliminate waste, 5S principles, and Kanban systems. On the other hand, Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) evaluates the environmental impacts by measuring energy and material consumption and waste generation.
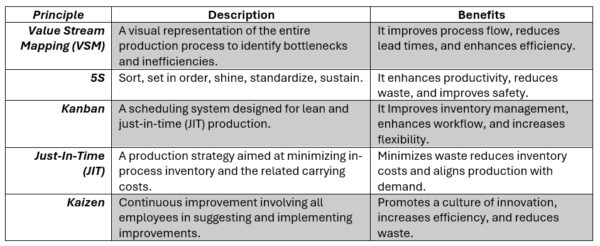
The five most important lean manufacturing principles. Inspired by Incorporating lean thinking and life cycle assessment to reduce environmental impacts of plastic injection moulded, own table design.
To read more: Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation
The LCA system assesses environmental impacts by analyzing data inputs from manufacturing processes, such as energy consumption, material usage, and time intervals. Additionally, this method entails setting objectives to evaluate a product’s environmental impacts and collecting inventory data. It also involves analyzing input and output data and interpreting the findings to understand environmental effects better.
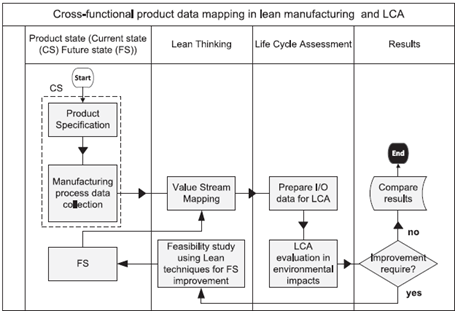
Integrating lean thinking and Life Cycle Assessment into the analysis of manufacturing environmental impacts. Courtesy of Incorporating lean thinking and life cycle assessment to reduce environmental impacts of plastic injection moulded products. Courtesy of Integrating lean thinking and Life Cycle Assessment into the analysis of manufacturing environmental impacts.
Driving Sustainability: A Case Study in Environmental Impact Reduction
A case study of a plastic casing product, conducted by the plastic injection moulding specialist Paramit in Malaysia showcased the efficacy of integrating Lean and Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) techniques.

A factory in the forest. Courtesy of Paramit.
By applying Lean methods alongside LCA, researchers achieved a 40% reduction in negative environmental impacts, including climate change, human toxicity, and acidification. Moreover, key improvements included a 90% reduction in production lead time, a 40% decrease in material usage, a 41% reduction in energy consumption, and a 32.3% cut in transportation requirements. This integrated approach provides a robust framework for making products more environmentally friendly.
To read more about this case of study: Journal of Cleaner Production and Paramit Manufacturing.
The research highlights the potential for significant improvements in the design and assessment of existing plastic products. The integration of Lean manufacturing techniques and Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) has proven highly effective in reducing the environmental impacts of the injection moulding process.
Future work should quantify the cost benefits of reducing environmental impact while exploring advanced methods like three-stage Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA). Additionally, adopting these integrated techniques can help manufacturers achieve substantial cost savings and comply with environmental regulations. Furthermore, these efforts will contribute to global sustainability initiatives and improve energy-intensive injection molding processes.
