Innovative Hydrogel Coatings for Medical Catheters
A recent study introduces hydrogel coatings for medical catheters to significantly reduce friction and prevent infections.
Healthcare professionals use medical catheters for delivering drugs, conducting surgeries, or draining fluids. These catheters, notorious for causing discomfort and infections, interact directly with body tissues and fluids. Consequently, traditional catheters, made from hydrophobic polymer materials, can cause high friction and increase the risk of bacterial colonization and blood clot formation.
You can also read: 3D-Printed Phantom Models for Medical Imaging
Hydrogel Coatings: A Dual-Function Innovation
Furthermore, researchers at Changchun University of Technology have developed a novel hydrogel coating that directly addresses these issues. They used a rapid polymerization process of acrylamide and sulfobetaine methacrylate, integrated with quaternary ammonium chitosan, to create a hydrogel coating for medical catheters that acts as a lubricant and possesses inherent antibacterial properties.
Hydrogel Preparation Process
The innovation starts with the application of a polyethyleneimine (PEI) adhesive layer, which enhances the catheter’s surface adhesion. Subsequently, researchers apply the hydrogel mixture and initiate a rapid cross-linking reaction with ferrous sulfate, creating a durable hydrogel layer within seconds. This method ensures a robust bond between the hydrogel and the catheter, significantly enhancing its functional lifespan and effectiveness.
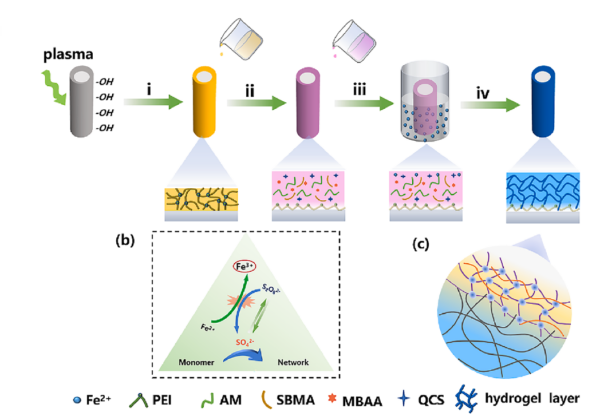
Schematic diagram of the detailed preparation process of the hydrogel coating. Courtesy of Fast-polymerized lubricant and antibacterial hydrogel coatings for medical catheters.
Performance and Benefits
The hydrogel-coated catheters demonstrate exceptional performance:
- Lubrication: The hydrogel reduces friction, making catheter insertion and use smoother and less painful for patients.
- Antibacterial and Antifouling Properties: Additionally, the hydrogel prevents bacterial growth and biofilm formation, crucial for reducing infection risks.
- Blood Compatibility: Moreover, the coating is designed to be compatible with blood, minimizing the chances of clot formation, a common issue with traditional catheters.
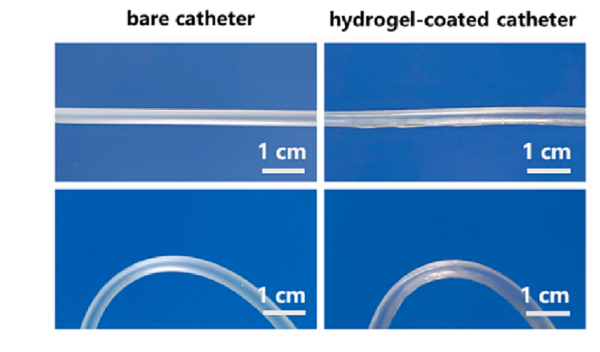
Photographs of a bare PVC catheter and a catheter coated with a hydrogel coating. Courtesy of Fast-polymerized lubricant and antibacterial hydrogel coatings for medical catheters.
Clinical Implications
The dual-functionality of these hydrogel coatings could revolutionize catheter use in medicine. Reduced friction and enhanced antibacterial properties greatly increase the safety and comfort of catheters, potentially reducing the incidence of catheter-related complications and improving overall patient outcomes. This technology also shows promise for broader applications in other medical devices that come into contact with body tissues.
Overall, researchers have developed lubricant and antibacterial hydrogel coatings, offering a significant advancement in medical device technology. As healthcare continues to advance, innovations like these play a crucial role in improving clinical outcomes and patient care quality, marking a significant step forward in medical treatment methodologies.
